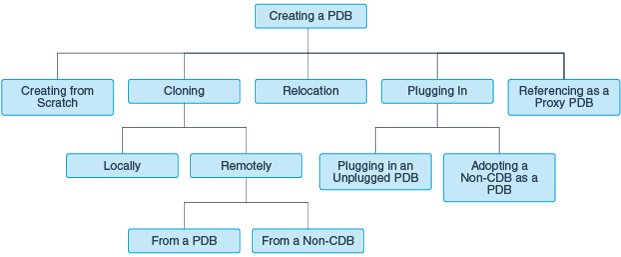
Techniques for Creating a PDB
| Technique | Description | More Information |
|---|---|---|
| Create a PDB from scratch | Create a PDB in a CDB using the files of the PDB seed or application seed. This technique copies the files associated with the seed to a new location and associates the copied files with the new PDB. This is the default creation mechanism. The other techniques require either a source database (PDB or non-CDB) or XML. | “Creating a PDB from Scratch“ |
| Clone an existing PDB or non-CDB | Create a PDB by cloning a source PDB or non-CDB. A source can be a PDB in the local CDB, a PDB in a remote CDB, a PDB in a local or remote application container, or a non-CDB. This technique copies the files associated with the source to a new location and associates the copied files with the new PDB. | “Cloning a PDB or Non-CDB“ |
| Relocate a PDB to a different CDB | Create a PDB by relocating it from one CDB to another. This technique moves the files associated with the PDB to a new location. | “Relocating a PDB“ |
| Plug an unplugged PDB into a CDB | Create a PDB by using the XML metadata file that describes the PDB and the files associated with the PDB to plug it into the CDB. | “Plugging In an Unplugged PDB“ |
| Reference a PDB as a proxy PDB | Create a PDB as a proxy PDB by referencing a different PDB with a database link. The referenced PDB can be in the same CDB as the proxy PDB, or it can be in a different CDB. | “Creating a PDB as a Proxy PDB“ |
| Create a PDB from a non-CDB, and then plug the PDB into a CDB | Create a PDB by adopting a non-CDB into a PDB. You can use the DBMS_PDB package to create an unplugged PDB from an Oracle Database 12c non-CDB. You can then plug the unplugged PDB into the CDB. | “Options for Creating a PDB from a Non-CDB“ |
PDB File Locations
In the CREATE PLUGGABLE DATABASE statement, you can specify the locations of files used by the new PDB.
The term “file name” means both the name and the location of a file. The CREATE PLUGGABLE DATABASE statement has the following clauses that indicate the file names of the new PDB being created:
- The
FILE_NAME_CONVERTclause specifies the names of the PDB’s files after the PDB is created.Use this clause when the files are not yet at their ultimate destination, and you want to copy or move them during PDB creation. You can use this clause in anyCREATE PLUGGABLE DATABASEstatement. - The
CREATE_FILE_DESTclause specifies the default Oracle Managed Files file system directory or Oracle ASM disk group for the PDB’s files.Use this clause to enable Oracle Managed Files for the new PDB, independent of any Oracle Managed Files default location specified in the root for the CDB. You can use this clause in anyCREATE PLUGGABLE DATABASEstatement.
When necessary, you can use both clauses in the same CREATE PLUGGABLE DATABASE statement. In addition, the following initialization parameters can control the location of the new PDB files:
- The
DB_CREATE_FILE_DESTinitialization parameter set in the root. This initialization parameter specifies the default location for Oracle Managed Files for the CDB. When this parameter is set in a PDB, it specifies the default location for Oracle Managed Files for the PDB. - The
PDB_FILE_NAME_CONVERTinitialization parameter. This initialization parameter maps names of existing files to new file names when processing aCREATE PLUGGABLE DATABASEstatement.
The following table shows the precedence order when both clauses are used in the same CREATE PLUGGABLE DATABASE statement, and both initialization parameters are set. For each clause and initialization parameter, the table also shows whether the files created by the CREATE PLUGGABLE DATABASE statement will use Oracle Managed Files or not.
Summary of File Location Clauses and Initialization Parameters
| Clause or Initialization Parameter | Precedence Order | Will the Files Created by CREATE PLUGGABLE DATABASE Use Oracle Managed Files? |
|---|---|---|
FILE_NAME_CONVERT clause | 1 | No |
CREATE_FILE_DEST clause | 2 | Yes |
DB_CREATE_FILE_DEST initialization parameter | 3 | Yes |
PDB_FILE_NAME_CONVERT initialization parameter | 4 | No |
Regarding the use of Oracle Managed Files, the table only applies to files created by the CREATE PLUGGABLE DATABASE statement. Files created for the PDB after the PDB has been created might or might not use Oracle Managed Files.
In addition, if FILE_NAME_CONVERT and CREATE_FILE_DEST are both specified in the CREATE PLUGGABLE DATABASE statement, then the FILE_NAME_CONVERT setting is used for the files being placed during PDB creation, and the CREATE_FILE_DEST setting is used to set the DB_CREATE_FILE_DEST initialization parameter in the PDB. In this case, Oracle Managed Files controls the location of the files for the PDB after PDB creation.
Clone Non-CDB to CDB
Set the DB_CREATE_FILE_DEST parameter on target so you don’t have to worry about FILE_NAME_CONVERT parameter during cloning or migration. Your target CDB will auto create the datafiles for cloned PDB into DB_CREATE_FILE_DEST parameter location
On target CDB: ============== SQL> alter system set DB_CREATE_FILE_DEST='/u01/CDB/';
On the source Non-CDB, create a user inside database and give permissions
On source Non-CDB: ================== SQL> create user migrate identified by migrate#123; SQL> grant connect, resource, create pluggable database to migrate;
On the target CDB, setup tns entries to connect source Non-CDB
On target CDB:
==============
NONCDB =
(DESCRIPTION =
(ADDRESS_LIST =
(ADDRESS = (PROTOCOL = TCP)(HOST = 3.19.61.169)(PORT = 1521))
)
(CONNECT_DATA =
(SERVICE_NAME = ORCL)
)
)
Create database link which allows us to connect source DB inside sqlplus on target
On target CDB: ============== SQL> create database link clone_link connect to migrate identified by migrate#123 using 'NONCDB';
Clone DB from source to target
On target CDB:
==============
SQL> create pluggable database ORCL from NON$CDB@clone_link;
SQL> create pluggable database {new-pdb} from {non$cdb}@{db-link};
Since there is no PDB to name, we use “NON$CDB” as the PDB name
execute the script noncdb_to_pdb.sql
SQL> @$ORACLE_HOME/rdbms/admin/noncdb_to_pdb.sql
SQL> SET SERVEROUTPUT ON
SQL> SET FEEDBACK 1
SQL> SET NUMWIDTH 10
SQL> SET LINESIZE 80
.
.
<output truncated>
.
.
SQL> set verify OFF
SQL> set wrap ON
SQL> set xmloptimizationcheck OFF
SQL>Clone PDB on Remote CDB
Set the DB_CREATE_FILE_DEST parameter on target so you don’t have to worry about FILE_NAME_CONVERT parameter during cloning or migration. Your target CDB will auto create the datafiles for cloned PDB into DB_CREATE_FILE_DEST parameter location
On target CDB: ============== SQL> alter system set DB_CREATE_FILE_DEST='/u01/CDB/';
On the source CDB, create a user inside PDB (you want to clone) and give permissions
On source PDB: ============== SQL> create user migrate identified by migrate#123; SQL> grant connect, resource, create pluggable database to migrate;
On the target CDB, setup tns entries to connect source PDB
On target CDB:
==============
SOURCE_HRPDB =
(DESCRIPTION =
(ADDRESS_LIST =
(ADDRESS = (PROTOCOL = TCP)(HOST = 3.19.61.169)(PORT = 1521))
)
(CONNECT_DATA =
(SERVICE_NAME = HRPDB)
)
)
Create database link which allows us to connect source PDB inside sqlplus on target
On source PDB: ============= alter pluggable database HRPDB open; On target CDB: ============== SQL> create database link HRPDB connect to migrate identified by migrate#123 using 'SOURCE_HRPDB'; SQL> select 1 from dual@HRPDB ;
Clone pdb from source to target
On target CDB:
==============
SQL> create pluggable database HRPDB_NEW from HRPDB@HRPDB;
SQL> create pluggable database {new-pdb} from {old-pdb}@{db-link};